Incoterms are revised and updated every 10 years.
Below is a quick guide of Incoterms 2020 which have come into effect as of January 1st 2020.
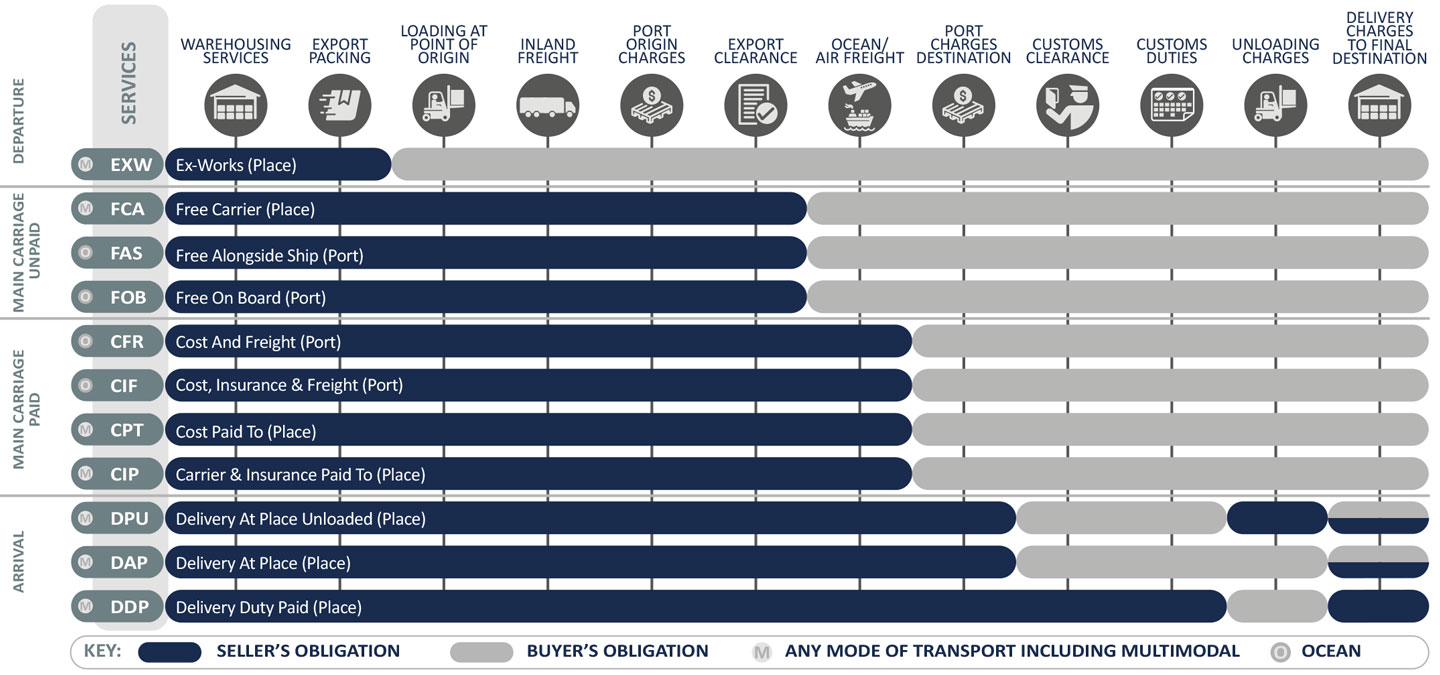
Incoterms® are the terms agreed upon by the seller and buyer during international transactions. These rules are globally recognized by governments and legal authorities.
They specify the point at which the seller’s costs and risks transfer to the buyer. It is important to note that not all rules apply universally; some cover various modes of transport. For example, FCA, CPT, CIP, DAP, DPU (which replaces DAT), and DDP apply to all transport modes (road, rail, air, and sea). Whereas Sea and Inland Waterway Transport are specifically addressed by FAS, FOB, CFR, and CIF.
International Commercial Terms, or Incoterms® are a set of rules issued by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) that relate to International Commercial Law.
According to the ICC, Incoterms® rules provide internationally accepted definitions and guidelines for the most common commercial terms used in sales contracts.
All international purchases are conducted based on an agreed Incoterm, which determines which party bears the costs and risks. These terms are clearly indicated on relevant shipping documents.
Understanding Incoterms® is essential in International Trade as they outline the specific tasks, costs, risks, and responsibilities of the buyer and seller in a sales contract.
Click on the card to expand it and see a detailed description
Ex works means the seller makes the goods available to the buyer at the seller’s location or another specified place (e.g., factory, warehouse). The seller doesn't need to load the goods or clear them for export.
The seller delivers goods to the carrier or a designated person at the seller’s location or another specified place. It’s crucial to clearly specify the exact delivery point, as the risk transfers to the buyer there.
The seller delivers when the goods are placed alongside the buyer's vessel at the named port. The risk of loss or damage passes to the buyer at that point, who then bears all costs.
The seller delivers the goods on board the buyer’s vessel at the named port or ensures they are delivered there. From that point, the buyer bears all costs and risks, including international transport, insurance, and further expenses. The seller covers costs up to loading, including delivery to the port, loading, and export duties. The buyer handles costs from loading to the final destination, such as freight, unloading, and import duties.
The seller delivers the goods on board the vessel and pays the cost and freight necessary to bring the goods to the named port of destination.
The seller delivers or ensures goods are on board the vessel. Risk transfers when goods are on the ship. The seller pays for costs and freight to the destination port, and contracts for minimum insurance cover against the buyer’s risk. The buyer must arrange additional insurance if needed.
The seller delivers the goods to the carrier or a nominated person at an agreed location. The seller covers the costs of carriage to the named destination.
The seller, as in CPT, also contracts for insurance covering the buyer’s risk during transit. Under CIP, the seller obtains only minimum insurance. For more coverage, the buyer must either agree on it with the seller or arrange additional insurance themselves.
The seller delivers when the goods are ready for unloading at the named destination. The seller bears all risks until then.
DPU replaces the old Incoterm® DAT (Delivered At Terminal). The seller delivers when the goods are unloaded and ready for the buyer at the named destination, bearing all risks until unloading is complete.
The seller delivers the goods when they are ready for the buyer, cleared for import, at the named destination. The seller bears all costs and risks until that point, including clearing the goods for export and import, and paying all duties and customs fees. Under DDP, the seller covers all shipping costs, including import customs clearance, duties, taxes, and additional delivery charges.