The EU Common Customs Tariff sets import duties for goods from non-EU countries and is updated annually. Customs classification is done during goods clearance.
TARIC is the Integrated Tariff of the EU, covering duties, suspensions, preferences, quotas, anti-dumping duties, and other trade measures.
TARIC codes are ten digits and can be accessed on TARIC Consultation.
The National Tariff combines TARIC with national taxes like VAT and excise duties.
Definition: Customs value refers to the transaction value, which is the price actually paid or payable for goods when sold for export to the EU. This includes costs like transport, insurance, commissions, royalties, etc., up to the first EU port of entry.
Can Customs Authorities Question the Customs Value? Yes, if Customs Authorities doubt the declared value's accuracy, they can request additional information from importers. If doubts remain, they may decide that the transaction value cannot be used.
Documents and Information Required by Customs Authorities:
Other documents may be required depending on the transaction, including ownership documents, quota payment invoices, advertising contracts, and financial documents related to interest charges or intellectual property rights.
The taxable value for VAT is composed of:
Excise Duties are indirect taxes imposed in all EU member states. They apply to products produced within a country as well as those coming from other EU member states or imported from third countries.
In Greece, all relevant European Directives and Regulations regarding Excise Duties have been incorporated into the National Customs Code (Law No. 2960/2001) as amended and in force, which governs the production, processing, possession, circulation, and control of products subject to these duties.
EU legislation determines which products are subject to excise duty and how this tax should be applied. It also sets minimum excise rates, although each EU country can set higher rates if it wishes. The payable tax is usually calculated based on quantity, e.g., per kilogram, hectoliter, or degree of alcohol. Excise Duties apply to the following products:
A key feature of excise duties is that they are paid when the products are made available for consumption.
The EMCS (Excise Movement and Control System) monitors the movement of excise goods (energy, tobacco, alcohol) within the EU under tax suspension. It replaces the Accompanying Administrative Document (AAD) with the e-AD, allowing real-time tracking and simplifying procedures. EMCS usage has been mandatory since 01-01-2011.
The process of importing or transferrring a passenger car or motorcycle for residents in Greece is outlined below
The registration tax for vehicles in tariff heading 87.03 is calculated as:
Registration Tax = (Retail Price Before Taxes - Discount for Used Vehicles) × Registration Tax Rate
A.1. Registration Tax Rates| Taxable Value (EUR) | Registration Tax Rate |
|---|---|
| 0 - 14,000 | 4% |
| >14,000 - 17,000 | 26% |
| >17,000 - 20,000 | 53% |
| >20,000 - 25,000 | 62% |
| >25,000 - 30,000 | 71% |
| >30,000 | 30% |
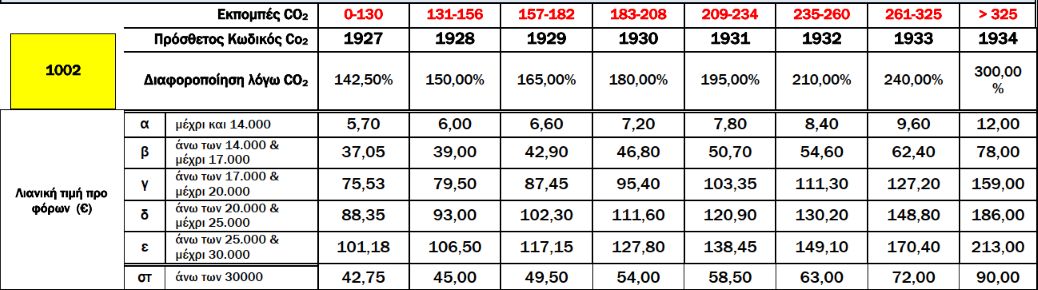
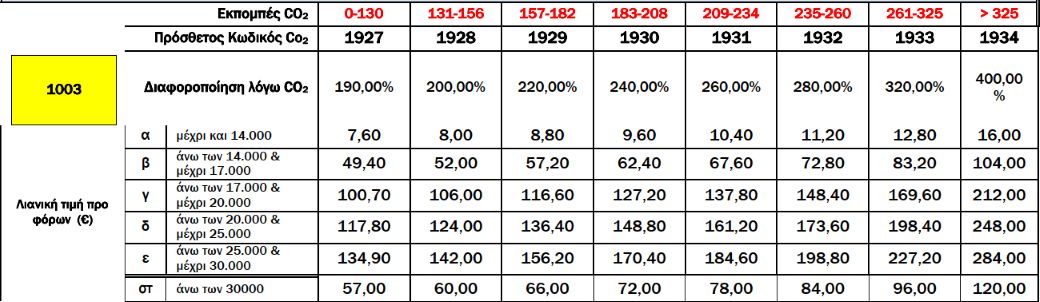
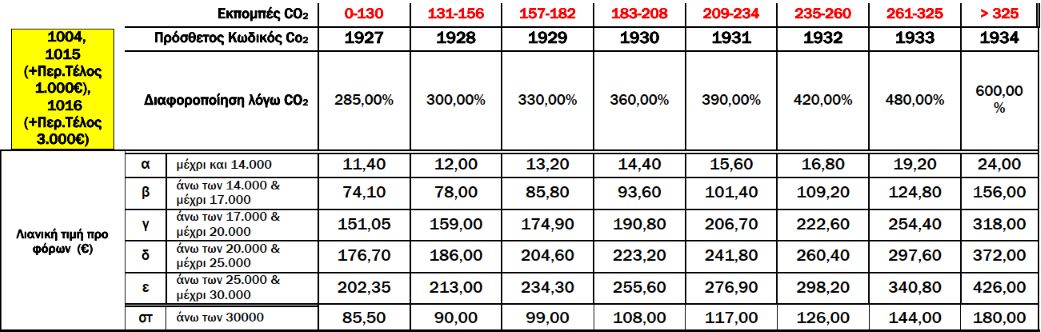
Rates further vary based on CO2 emissions and EURO standards.
A.2. Variation of Registration Tax Rates Based on CO2 EmissionsFrom 01.01.2021, two scales of CO2 emissions values are used to calculate the increase or variation in registration tax rates, depending on the first registration date of passenger cars in the EU, and the method of measuring CO2 emissions [according to the New European Driving Cycle (NEDC) or the Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicles Test Procedure (WLTP)]. Specifically:
Additionally, registration tax rates for passenger cars vary further based on EURO emission standards, as defined by respective Regulations or Directives. For specific cases:
For cars not meeting any EURO standards or without proven CO2 emissions, tax rates are increased by 200% plus an additional 100%. An environmental fee is also imposed on used passenger cars.
Environmental Fee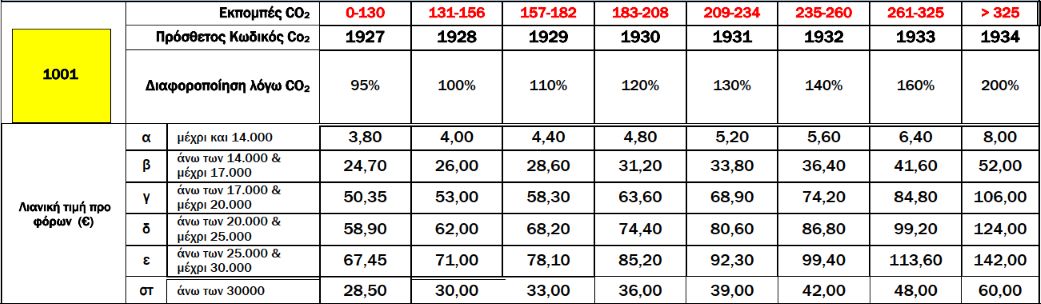
Hybrid motor vehicles with CO2 emissions ≥51 g/km are exempt from 50% of the registration tax. Those with emissions ≤50 g/km are exempt from 75%.
Fully electric cars are exempt from the registration tax.
Motorhomes are exempt from 75% of the registration tax.
CO2 emissions and EURO standards are verified by the customs authority, based on the type approval and compliance certificate.
For used vehicles, the original registration certificate from the foreign country is required.
The taxable value for the registration tax of passenger cars is based on the retail price before taxes, by type, variant, and edition, as submitted by official car dealers to the relevant Customs Authority, including the value of optional equipment. For used cars, the retail price before taxes of a similar new car is considered, reduced by depreciation rates based on age and body type.
Depreciation Rates for Used Cars| Years | 4x4 (SUV – ATV) | Hatchback | Sedan | Cabrio | Coupe-Roadster | MPV |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 11% | 9% | 15% | 11% | 12% | 9% |
| 1 | 22% | 19% | 30% | 22% | 25% | 19% |
| 1.5 | 25% | 24% | 33% | 26% | 25% | 23% |
| 2 | 29% | 28% | 36% | 30% | 29% | 27% |
| 2.5 | 35% | 32% | 40% | 33% | 32% | 33% |
| 3 | 37% | 37% | 43% | 36% | 36% | 36% |
| 3.5 | 44% | 43% | 50% | 42% | 41% | 43% |
| 4 | 50% | 49% | 57% | 48% | 47% | 49% |
| 4.5 | 56% | 55% | 64% | 54% | 53% | 55% |
| 5 | 62% | 61% | 72% | 60% | 59% | 61% |
| 5.5 | 66% | 64% | 74% | 64% | 63% | 64% |
| 6 | 68% | 67% | 76% | 67% | 66% | 67% |
| 6.5 | 71% | 70% | 78% | 69% | 68% | 70% |
| 7 | 73% | 72% | 80% | 72% | 71% | 72% |
| 7.5 | 75% | 74% | 81% | 74% | 73% | 75% |
| 8 | 77% | 76% | 83% | 76% | 75% | 77% |
| 8.5 | 79% | 78% | 84% | 78% | 77% | 78% |
| 9 | 80% | 80% | 85% | 79% | 79% | 80% |
| 9.5 | 82% | 81% | 86% | 81% | 80% | 82% |
| 10 | 83% | 83% | 87% | 82% | 82% | 83% |
| 10.5 | 84% | 83% | 88% | 83% | 83% | 84% |
| 11 | 85% | 84% | 89% | 84% | 84% | 85% |
| 11.5 | 86% | 85% | 89% | 85% | 85% | 86% |
| 12 | 87% | 86% | 90% | 86% | 86% | 87% |
| 12.5 | 88% | 87% | 90% | 87% | 87% | 88% |
| 13 | 88% | 88% | 90% | 88% | 87% | 89% |
| 13.5 | 89% | 89% | 91% | 88% | 88% | 89% |
| 14 | 90% | 89% | 91% | 89% | 89% | 90% |
| 14.5 | 90% | 90% | 91% | 89% | 89% | 91% |
| 15 | 90% | 90% | 91% | 90% | 89% | 91% |
| 15.5 | 90% | 90% | 91% | 90% | 89% | 91% |
| 16 | 95% | 95% | 95% | 95% | 95% | 95% |
The taxable value, after the above depreciation, is further reduced by a percentage using a coefficient of 0.10 for every additional 500 kilometers traveled above the annual average.
The depreciation based on kilometers traveled should not exceed 10% of the value determined after the above depreciation.
The annual average mileage is set at fifteen thousand (15,000) kilometers.
The total depreciation, including that due to mileage beyond the average, cannot exceed 95%.
For passenger cars imported from non-EU countries, a 10% import duty is imposed on the customs value. However, for countries with preferential agreements with the EU, this duty can be reduced or zero.
(C) VAT for VehiclesFor VAT application in Greece, "vehicles" are defined as land vehicles with engines over 48 cc or power over 7.2 KW, intended for transporting people or goods.
a) For vehicles imported from non-EU countries:Imported passenger vehicles are subject to a 24% VAT on the taxable value. The taxable value for VAT calculation includes the customs value, duties, and taxes owed inside or outside Greece (excluding registration tax and VAT), and ancillary import costs if not included in the customs value, such as transport, loading, unloading, and insurance costs.
b) For vehicles from other EU countries:If the cars are new (i.e., have traveled less than 6,000 km or are within six months from the first registration date), they are subject to a 24% VAT in Greece. The taxable value for VAT calculation is the purchase price from the invoice, plus any additional fees or expenses directly related to the purchase, and any taxes collected for the public or third parties (excluding registration tax and VAT).
For new cars, if the buyer has paid VAT in the country of purchase, they can apply for a certificate from the Greek Customs Authority to claim a VAT refund from the country of purchase (if the country's legislation allows).
If the cars are used (i.e., have traveled more than 6,000 km and are over six months from the first registration date), no VAT is paid in Greece but in the country of purchase. For private sales agreements, the document must be authenticated by the Greek Consulate in the seller's EU country, with the buyer present.
Required documents for Import of Passenger CarsThe indicative required documents for customs clearance, both for choosing the registration tax rate and for determining the taxable value, are as follows:
Luxury Tax is imposed on the following items:
| ITEM | LUXURY TAX RATE |
|---|---|
| a) Reptile, crocodile, lizard, and wild animal skins in general, as well as birds, fish, and sea animals, treated or untreated. HS Codes: 41.06.40, 41.13.30, EX41.14.10.90, 4103.20, EX 4103.90, EX 4106.91, EX 4106.92 | 10% |
| b) Leather goods from item a. HS Codes: 42.02.21.00, 42.02.31.00, 42.03.30.30 | 10% |
| c) Leather shoes from item a. HS Code: 64.03 | 10% |
| d) Clothing, accessories, and other items from fur skins. HS Code: 43.03 | 10% |
| e) Carpets from any material containing silk or silk waste over 10% of total weight. HS Codes 57.01.10.10, 57.01.90.10 | 10% |
| f) Raw or processed pearls, precious or semi-precious stones, synthetic or reconstituted stones, treated or untreated. Excludes those for industrial use. Diamonds even if processed. HS Codes: 71.01, EX 71.02, EX 71.03, 71.04 | 10% |
| g) Diamond dust and powder from precious or semi-precious stones, natural or synthetic. HS Code: 71.05 | 10% |
| h) Jewelry with or without precious stones and parts thereof, from precious metals or metals plated with precious metals. HS Code 71.13 | 10% |
| i) Goldsmith items and parts thereof from precious metals or metals plated with precious metals. HS Code: 71.14 | 10% |
| j) Other artifacts from precious metals or metals plated with precious metals. HS Code 71.15 | 10% |
| k) Artifacts from pearls, precious or semi-precious stones, or synthetic or reconstituted stones. HS Code 71.16 | 10% |
| l) Private aircraft, seaplanes, and helicopters. HS Code: 88.02 | 20% |
| m) Watches from precious metals or metals plated with precious metals. HS Code: 9101 | 10% |
| n) Watch cases from precious metals or metals plated with precious metals. HS Code: 9111.10 | 10% |
| o) Watch bracelets from precious metals or metals plated with precious metals. HS Code: 9113.10 | 10% |
For items from non-EU countries, the luxury tax is confirmed and collected by customs upon consumption, while for items from other EU countries or domestically produced, the tax is paid to the competent tax office at the location of the entrepreneur's headquarters.
Items of cases h, i, j, and k with a taxable value of less than €1,000 per piece are exempt from the luxury tax. Also exempt are items from cases h, i, and j from silver in HS Code 71.13, 71.14, and 71.15.
The luxury tax on transport means in case l, regardless of the country of origin, is confirmed and collected by customs authorities along with other tax liabilities. The taxpayer for domestically produced items is the producer, while for items from other EU countries, it is the person making the intra-community acquisition.
The EORI number is a unique identifier assigned by Customs Authorities in EU Member States to economic operators involved in customs-regulated transactions. Once issued, it is used in all dealings with the customs authorities across the EU.
The EORI number ensures efficient implementation of security measures introduced by Council Regulation (EC) No 648/2005 and its Implementing Provisions (Regulation (EC) No 1875/2006). It allows immediate identification of economic operators across the EU. The EORI number is defined in the Union Customs Code, Regulation No 952/2013.
All EORI numbers issued by the Customs Authorities of Member States are stored in a central database overseen by the EU. The EOS records the identification data of economic operators as specified in Annex 12-01 of Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/2446.
The unique EORI number is used in all transactions with the customs authorities of EU Member States, such as submitting data before the arrival and departure of goods entering or leaving the customs territory of the Union, during import and release for free circulation, export, and transit procedures. It is also used for exchanging information about the movement of goods between customs authorities.
The AEO license is for economic operators involved in transactions governed by customs regulations. Authorized Economic Operators (AEOs) are seen as reliable business partners in the international supply chain. This reliability is certified by Customs Authorities through the AEO license, which requires and implies close cooperation with customs, taking on significant responsibilities for safeguarding fiscal interests, protecting the environment, and ensuring citizen safety.
In return, Customs Authorities provide AEOs with significant benefits, including easier and immediate access to customs simplifications, faster processing of customs transactions, immediate release of financial resources by reducing guarantees for customs procedures, expedited VAT refunds under certain conditions, international recognition through mutual AEO recognition agreements with third countries, and enhanced credibility via the right to use the AEO logo, which strengthens their market position and helps find new customers.
The REX system is a new self-certification system for the origin of goods by exporters, established by the EU based on the Union Customs Code - Regulation (EU) 952/2013 and Implementing Regulation (EU) 2447/2015. The REX system simplifies export procedures. Exporters no longer need to visit Customs to issue a certificate of origin for each export, as they can certify the origin of goods by making a specific declaration on the invoice or another commercial document, called a "Statement of Origin."
To be eligible to make a "Statement of Origin" for shipments over €6,000, the exporter must be registered by the competent customs authorities in an electronic registry created by the European Commission. This registration grants them the status of a registered exporter. The €6,000 threshold applies to all Agreements using the REX system, except for Overseas Countries and Territories, where the limit is €10,000.
The Registered Exporter System (REX) was initially implemented from 01-01-2017 only in the group of countries within the Generalized System of Preferences (GSP) and does not modify the rules of origin acquisition, only the method of certification. It is now also applied within other Preferential Agreements such as: the EU-UK Trade and Cooperation Agreement (from 01/01/2021), the EU-Canada Comprehensive Economic and Trade Agreement (CETA) (from 21/09/2017), the EU-Japan Economic Partnership Agreement (from 01/02/2019), the Interim Economic Partnership Agreement between the EU and the states of Eastern and Southern Africa (ESA) (from 01/09/2020), the EU-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement (from 01/08/2020), and the EU Council Decision on the association of Overseas Countries and Territories (OCT) (from 01/01/2020).
Procedure for VAT refund or exemption for purchases made by travelers who are residents of non-EU countries and take the goods with them when leaving for non-EU countries:
Travelers not residing within the EU are entitled to a VAT exemption for goods purchased in the EU, intended for personal or family use, and carried in their personal luggage when leaving for a non-EU country. The exemption can be direct or indirect.
(A) Conditions for Exemption:The receipt must be stamped by Customs at the last point of departure. The VAT refund is processed by the Greek seller directly or through an intermediary.
(D) When buying goods in another EU country and leaving for a non-EU country from Greece:The receipt is stamped by Greek Customs at departure. The VAT refund is processed by the seller in the other EU country.
Foreigners or Greeks residing abroad who move to Greece permanently can import personal items (household goods, car, etc.) duty-free. This includes Greek political refugees returning to Greece. To qualify, they must have resided abroad for at least the last two years before moving, proven by a Resettlement Certificate from the Greek Consulate.
Usual Residence is defined as the place where a person stays for at least 185 days per year due to personal and professional ties. For those without professional ties, it’s determined by personal ties. Students abroad do not qualify. Proof includes staying 185 days annually and having personal or professional ties.
How to prove personal and professional ties?Professional ties are proven by occupation, and personal ties by family and other permanent connections. Required documents may include:
Personal items include:
A Transit Log (Movement Permit) for private leisure boats under temporary importation, is granted to non-EU flagged private pleasure boats longer than 7 meters, with or without accommodation facilities, designed exclusively for leisure or touring purposes, as long as they are not classified as commercial and fall under the temporary importation regime.
The requirements for issuing a Transit Log for private leisure boats are:a) For private leisure boats longer than 7 meters, flying a non-EU flag, and operated by a person residing outside the EU, a Transit Log valid for 18 months is issued by the relevant Customs Authority. Upon expiration, the boat must be re-exported, and the Movement Permit submitted to the Customs Authority.
b) Private leisure boats under 7 meters in length, subject to temporary importation, receive a Temporary Importation Permit (ΔΕ.Π.Ε.), similar to other vehicles under temporary importation (e.g., cars, motorcycles), and not a Transit Log.
Categories of Ships Eligible for Duty-Free Fuel
Under current regulations, the following categories of ships are exempt from excise tax on fuel:
The fuel supply is based on necessity, determined by the duration of the voyage, the number of passengers, the type of ship, and the fuel tank capacity. Documentation and entries in the Duty-Free Book are required.
Fuel supply at Customs:
As per Circular ΔΔΘΤΟΚ Γ 1151184 ΕΞ2016/ 20-10-2016, updated by ΔΔΘΤΟΚ Γ 1158944 ΕΞ2016/ 4-11-2016, necessary documents include:
Fishing boats in Greek waters receive duty-free fuel for three months, based on the boat’s category and engine power. Duty-free status is verified through the Duty-Free Book and ship's logbook, approved by relevant authorities and kept onboard.
Fuel Supply with Tax Refund ProcedureFuel from taxable stocks is allowed only if duty-free fuel isn’t available, or special circumstances apply, as determined by the relevant Customs Office. The application for an excise tax refund is submitted online four times a year (end of January, April, July, and October) or semi-annually (end of July for the first half and end of January for the second half).
Necessary documents include:
The Duty-Free Book is issued and validated by the Customs Authority in the region where the applicant is based. This is done upon submission of an application and a receipt from the tax office for the equivalent value payment. The general management of Duty-Free Books belongs to the A' Customs Office of Import, Excise Duties, and Supplies in Piraeus.
The Temporary Import and Use regime allows individuals to import and use their transport means and belongings temporarily while in Greece
Eligible persons include:
A) Residents abroad visiting Greece temporarily (Tourists):
B) Residents in Greece working abroad for at least 6 months per year:
C) Greek crew of international commercial ships:
D) Special categories:
Transport items:
Personal items:
Note:Passenger vehicles entering Greece must have official regular or temporary license plates from the country issuing their registration. They must also be accompanied by a registration certificate from the issuing country and be insured. If the temporary registration is invalid upon entry, the vehicle cannot be temporarily imported. Additionally, they cannot remain or circulate in Greece beyond the temporary registration's validity date. To continue their stay, owners must obtain Greek temporary plates and registration from the Customs Authority. The eligible person must have a passenger vehicle driver's license.
The ATA Carnet is an international customs document and guarantee for facilitating goods movement between the EU and third countries, allowing temporary import/export without paying customs duties and taxes.
In Greece it is Issued by the Chambers of Commerce and Industry to eligible individuals.
Conditions for issuance:The Processing for Re-Exportation (Active Processing) regime aims to promote exports to third countries and enhance the competitiveness of the EU manufacturing industry globally.
The advantage is that the regime exempts non-EU goods from duties when imported into the EU for processing and re-exported as derivative products. Alternatively, these goods can be released for free circulation in the EU, subject to duties and taxes applicable at the time of customs debt.
It is available to individuals or companies established within the EU, with the following conditions:
The regime is finalized when processed goods enter another customs regime, leave the EU, are destroyed without residue, or are abandoned to the state.
The Processing for Re-Importation (Passive Processing) regime allows for the temporary export of Union goods to non-EU countries for processing and the re-importation of the processed products. The customs debt is calculated based on the processing costs incurred outside the EU customs territory.
The advantages of this regime are that it allows beneficiaries to take advantage of lower labor costs outside the EU, encourages the use of Union raw materials in the production of final products, and provides favorable tariff treatment for re-imported goods. Additionally, under the "standard exchanges" system, there is an option to return a product to a third country for repair or replacement with another product (replacement product).
Approval for the regime is granted to natural or legal persons established in the EU, provided they meet the guarantees required by the Customs Authority.
the permit is issued after an examination of the application and accompanying documents. Customs Authorities may refuse to issue a permit for sensitive agricultural products listed in Annex 71-02 of Regulation (EU) 2446/2015 if it is shown that the processing could harm the essential interests of Union producers.
The permit is valid for up to five years, or up to three years for sensitive agricultural products listed in Annex 71-02 of Regulation (EU) 2446/2015.
The taxable value of re-imported items is determined by the provisions related to the regime, taking into account the added value of the service provided in the third country (According to paragraph 2 of Article 20 of Law 2859/2000).
Special Destination is a customs regime that allows the placement of imported (non-EU) goods into free circulation and consumption with full or partial suspension of customs duties, i.e., with favorable tariff treatment due to their specific use. This favorable tariff treatment applies only to the conventional duty of the Common Customs Tariff and does not exempt from any anti-dumping duties, VAT, etc.
When goods are placed into free circulation with a reduced or zero import duty due to their special use, they remain under customs supervision. This supervision ends when the conditions for granting the reduced or zero duty no longer apply, when the goods are exported or destroyed, or when it is permitted to use the goods for purposes other than those for which the reduced or zero import duty was granted, upon payment of the owed duties.
The Special Destination regime is provided for the following categories of goods:The importer/exporter or their legal representative / customs broker, must electronically submit the import/export declaration through the Imports-Exports Subsystem of the Integrated Customs Information System ICISnet to the Customs office with the respective jurisdiction. Submission of a declaration is also required when importing/exporting goods to territories that are part of the customs, but not the fiscal area of the EU.
The declarant or their legal representative must be aware of the necessary fields and entries required to complete the declaration, depending on the customs regime under which the goods are to be placed, according to applicable regulations (Articles 158-162, 170 of Union Customs Code Regulation 952/2013). Submitting a declaration to Customs, as per Article 15 of the Union Customs Code Regulation 952/2013, commits to the accuracy of the declaration and compliance with all obligations regarding the customs regime of the goods.
The declaration must be accompanied by supporting documents submitted electronically (in digital form), necessary for the application of the provisions governing the requested customs regime (e.g., invoice, transport documents, packing list, certificates/licenses/approvals – see also response to question 189). Specifically, concerning export and VAT exemption, a valid document for VAT exemption includes the printout of the IE599 "Export Completion Notification" message from the exporter/declarant's environment. The Customs endorsement for this printout has been abolished as tax offices can monitor exports through their system.
Instructions and analysis of related electronic messages for the operation of the ICISnet Import Subsystem are provided by circular Δ19Α 5041357 ΕΞ2013/28-11-2013 (ΑΔΑ: ΒΛ12Η-ΑΝΝ) of the Head of the General Directorate of Customs and Excise. Further instructions on the mandatory electronic submission of supporting documents for import declarations are provided by circular ΔΤΔ Α 1019512 ΕΞ 2017/03-02-17 (ΑΔΑ: 6Ε8ΞΗ-ΟΦΧ) of the A.A.D.E. Commander, which communicated the decision ΔΤΔ Α 1184721 ΕΞ2016/16-12-2016 (Β’ 4488, ΑΔΑ:7ΦΗΝΗ-2Η3) of the General Secretary of Public Revenue. Instructions in line with the Union Customs Code regarding the export regime and compliance with export formalities are provided by circular ΔΤΔ Α 1068392 ΕΞ2016/ 26-4-2016 (ΑΔΑ: ΩΨΜ6Η-ΔΡΧ) of the Head of the General Directorate of Customs and Excise. Additional instructions on the mandatory electronic submission of supporting documents for export declarations are provided by circular ΔΤΔ Α 5022456 ΕΞ 2015/23-10-2015 (ΑΔΑ:ΒΜΞΠΗ-ΡΥ0) of the Head of the General Directorate of Customs and Excise, which communicated the decision ΔΤΔ Α 117 5016701 ΕΞ2015/31-7-2015 (Β’ 1698, ΑΔΑ: ΩΖ36Η-0Ε6) of the General Secretary of Public Revenue.
According to National Legislation (Law 718/1977 - A’ 304 "Regarding Customs Brokers"), as amended, a legal representative of the declarant can be any natural, legal person, or association of persons.
Documents required for customs clearance:Note: Non-commercial small consignments" are parcels that (a) Are occasional in nature, (b) Are intended for personal or family use by the recipients and do not raise doubts about their non-commercial nature due to their nature or quantity. (c) Are sent without any payment from the recipients.
Prohibitions and Restrictions: Prohibitions and restrictions concern measures established for public policy or security reasons and are imposed on the cross-border movement of goods between the EU and third countries to protect the health and lives of citizens, animals, and plants, the environment and to preserve cultural heritage.
The Customs service, has a comprehensive view of the goods flows crossing the EU's borders, thus they are tasked with ensuring compliance with prohibitions and restrictions imposed by EU and national regulations during customs formalities.
These regulations often involve issuing a license/certificate/approval upon the applicant's request by the competent national or EU authority. Therefore, the interested economic operator must secure the necessary license/certificate/approval ("supporting document") from the competent authority before importing or exporting goods to and from third countries. This document must be declared in the customs declaration for acceptance by the ICISnet Customs Information System, and Customs, upon verifying the necessary prohibitions and restrictions, will allow the import/export.
Customs Warehousing and Storage is a special regime that allows the entry and storage of non-Union goods in customs-approved warehouses without paying duties and taxes until the regime is cleared. To withdraw goods for consumption, applicable duties and taxes must be paid.
Businesses such as importers, storage companies, transportation firms, and supply companies can apply to establish a customs or bonded warehouse
The requirements for establishing a customs or bonded warehouse include:Any goods, provided necessary permits for hazardous items concerning public order, safety, health, and environment are obtained.
Entry of Goods in the customs warehouse:Goods are presented to Customs with a storage declaration. After Customs inspection, a receipt permit is issued, allowing goods to be stored.
Regime clearance:The regime is cleared by re-exporting goods or placing them under another customs procedure (e.g., free circulation and consumption, transit, processing for re-export). Goods can also be destroyed or abandoned to the state.
Exit of Goods from the customs warehouse:Goods must be declared for another customs procedure or re-exported. Customs performs necessary checks and issues a receipt permit for goods to exit.
Governing regulation: Articles 210 to 225 (horizontal provisions of special regimes) and 237 to 242 of Reg. (EU) 952/13.
Free Zones (FZ) are special regimes operating in parts of the customs territory of the Union, separated from the rest of that territory.
Within these zones, Non-EU goods entering are not subject to customs duties, taxes, and other charges, as well as commercial policy measures, provided these measures do not prohibit the entry/exit to/from the EU customs territory.
The primary purpose of establishing a Free Zone is the storage of non-EU goods and facilitating international trade while safeguarding fiscal interests.
Goods entering the FZ are subject to restrictions if entry into the Union's customs territory is prohibited by relevant decisions.
Goods consumed or used within the FZ must pay the due import duties and taxes before consumption or use.
Industrial, commercial, or service activities are allowed within the FZ, with prior notification to customs authorities. Various businesses can operate within the FZ, provided they maintain an accounting warehouse approved by the relevant Customs Region.
The regulation governing the Free Zones, establishment and operation can be found in: Articles 210 to 225 (horizontal provisions of special regimes) and 237 to 239, 243 to 249 of Regulation (EU) 952/13 for the establishment of the Union Customs Code.
Third-country goods transported by road within the EU must be placed under the Union transit regime, unless passing through a third country, where the TIR regime may be used. The "holder of the procedure" presents the goods to the departure Customs office, submits the electronic transit declaration, and provides a guarantee based on duties and taxes.
Differences between TIR and Union/Common Transit (T1):Relevant legislation regarding refunds of undue customs duties:
Definition: Customs duties are considered undue when, at the time of payment, they were not legally owed.
Identification: Undue payments can be identified by the payer or the Customs Authority.
Judicial Confirmation: Undue payments can be recognized and confirmed by a decision from the Administrative Court.
Application for refundApplications for refunds can be submitted by the payer or their legal representative within three years from the date of recognition of the undue payment. Necessary documentation must be attached. If identified by Customs, the payer is invited to apply within the same period. For judicial decisions, applications must be submitted within one year from the decision date if not already ordered by the court, or within five years if ordered by an appellate court.
Types of Customs Offences:
Criminal prosecution ceases if the offender pays a double (instead of triple) fine and meets specific conditions:
Definition: A customs broker is a natural person who has obtained a customs broker certification and primarily conducts customs clearance procedures in the context of customs representation. Customs brokerage firms are legal entities primarily engaged in customs clearance procedures in the context of customs representation, employing or involving at least one certified customs broker. Detailed instructions on customs representation, and access to and practice of the customs brokerage profession, are provided in Circular No. D19Γ 5044128 ΕΞ 2012 / 23-11-2012 by the Directorate of Customs Procedures (D19).
Any "natural or legal person or association of persons" can appoint a customs representative to handle the required actions and formalities according to customs legislation in transactions with Customs Authorities. This representation can be either direct, where the customs representative acts in the name and on behalf of the represented party, or indirect, where the customs representative acts in their own name but on behalf of the represented party. The customs representative must be established in the customs territory of the European Economic Area (EEA) and have an EORI number and an active Greek VAT number. In transactions with Customs Authorities, the customs representative must declare they are acting on behalf of the represented party and specify whether the representation is direct or indirect. Customs Authorities may request a written authorization from any person claiming to act as a customs representative.
Customs Clearance Procedures are the actions and formalities required by customs legislation in transactions with Customs Authorities. These include any procedures that deal with the declaration and control regarding the movement of goods, payment of taxes and duties and applications for customs regimes amongst others.
1. REGULATION (EU) No 952/2013 OF THE EUROPEAN PARLIAMENT AND OF THE COUNCIL
2. Commission Delegated Regulation (EU) 2015/2446 of 28 July 2015
3 Commission Implementing Regulation (EU) 2015/2447 of 24 November 2015
4. LAW 2960/2001 Greek National Customs Code
5. Independant Authority for Public Revenue (AADE) Customs Information for Traders